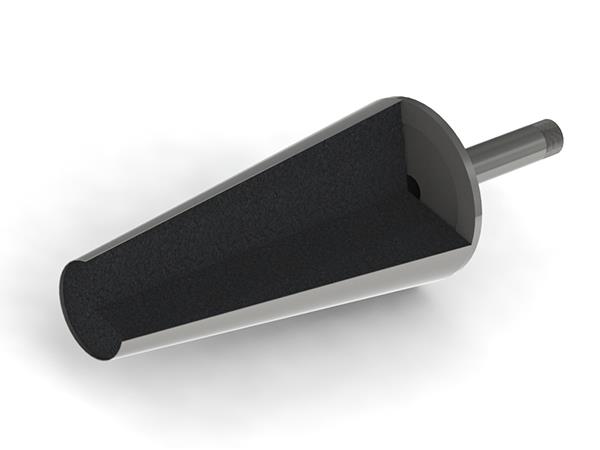
Introduction to the use performance of breathable bricks
Breathable brick is a new product with high lifespan, energy saving and consumption reduction, reasonable structure design, good thermal stability, erosion resistance, erosion resistance, and permeability resistance, high blow-through rate, safe and reliable operation, and long service life. Features.
Slag resistance
In order to improve the material's slag resistance and resistance to molten steel penetration, Cr2O3 or part of chromium corundum is usually added to the corundum spinel permeable brick. Cr2O3 and a-Al2O3 have the same crystal structure, Cr2O3 not only improves the material's performance The slag resistance increases the wetting angle between the material and the molten steel, and has a significant improvement in the blockage of the pores of the breathable brick due to the penetration of the molten steel.
The aluminum-chromium solid solution and the independent chromium-containing glass phase formed by Cr2O3 fine powder and Al2O3 at high temperature are used to form a liquid phase with a certain viscosity when it contacts with the slag in the molten steel smelting process, thereby hindering the molten steel slag. At the same time, it can absorb iron oxide and magnesium oxide in the slag, and form a dense spinel in the working layer of the breathable brick, which improves the slag resistance of the breathable brick.
However, when Cr2O3 is added to the material, after high temperature firing or use, Cr3 is oxidized to Cr6, and Cr6 is toxic and will pollute the environment. Therefore, in order to save energy and protect the environment, Cr2O3 should be avoided as much as possible, and by replacing raw materials, the The high temperature performance after adding Cr2O3 reaches the level of adding Cr2O3.
Thermal shock resistance
breathable brickThe main damage method is thermal shock damage. With the continuous increase of the tapping temperature, there is a large temperature difference between the working surface of the breathable brick and the intermittent, which requires the material to have extremely high thermal shock resistance. In the castable The introduction of spinel phase can improve the thermal shock resistance of breathable bricks.
The oxide or non-oxide added to the breathable brick forms a solid solution phase with the aggregate at high temperature, which increases the high temperature strength of the brick, improves the permeability of the brick, and resists the erosion of the slag in the ladle to the breathable brick. After the brick is heat treated at high temperature, its performance is improved to meet its use requirements.

Related News
- Introduction of construction method of ramming material in intermediate frequency furnace
- How to choose the material of furnace lining
- The difference between rammer and castable
- Application direction of intermediate frequency furnace refining
- Introduction to the construction method of dry ramming material
- Do you know the production process and control points of breathable bricks?
- The application of argon blowing technology at the bottom of the intermediate frequency furnace
- Method for prolonging service life of intermediate frequency furnace lining
- In addition to diffused breathable bricks, there are those types of breathable bricks
- What are the advantages of coil cement
- Some points that should be paid attention to in the furnace lining construction of the intermediate frequency furnace
- What are the advantages of qualified intermediate frequency furnace linings?
- Cause Analysis of Damaged Furnace Lining
- Introduction of chemical erosion of ramming material in intermediate frequency furnace
- Introduction to the construction method of smearing ramming material
- How to improve the argon blowing rate of ladle breathable bricks
- The correct operation plan of the ramming material used in the bottom of the electric furnace
- What is the material of the intermediate frequency furnace lining
- How to remedy cracks in ramming material
- Introduction to the solution to cracks in the ramming material of the intermediate frequency furnace