How to choose zirconium ramming material for glass kiln bottom
Zirconium ramming material is a kind of amorphous refractory material with low plasticity. It is mainly composed of zirconium aggregate, powder, binder and additives. It is mixed well according to a certain proportion and then rammed into shape. It is widely used in glass furnace pools. Bottom sealing and heat preservation. When different zirconium ramming materials are corroded by different components of glass liquid, the physical and chemical reactions that occur are not completely consistent. Therefore, according to the glass components melted in different furnaces, appropriate Zirconiumramming material, in order to achieve the effect of matching application. Today, Xiaobian will give us a specific explanation on how to choose different zirconium ramming materials?
1,2 kinds of commonly used zirconium ramming materials and their functional advantages
The ability of refractory materials to resist high temperature glass liquid corrosion is an important factor in determining the life of glass furnaces and the quality of glass products. Zirconium ramming materials can be widely used in the bottom of glass furnace pools. In addition to its strong properties, it also benefits from the superior corrosion resistance and ultra-high refractoriness of zirconium materials. Zirconium aggregates are the skeleton of zirconium ramming materials and play an important role in the high temperature physical properties of zirconium ramming materials. As a result, at present, there are mainly two kinds of zirconium ramming materials used at the bottom of glass furnaces in China: one is fused AZS ramming material, and the other is zircon ramming material.
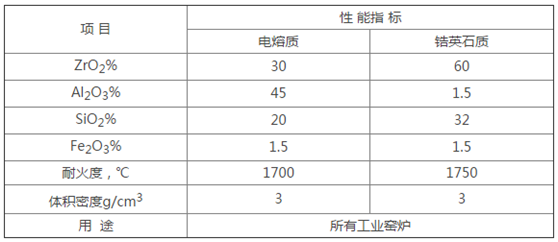
The fused AZS ramming material is made by breaking the fused zirconium corundum brick into particles of about 5mm as aggregate, and then mixed with other auxiliary materials. It retains the advantages of the fused zirconium corundum brick and has strong corrosion resistance to glass liquid , The porosity is small, the performance is extremely stable, and the intrusion of molten glass and metal can be well inhibited. The zircon ramming material is a certain proportion of destroyed sintered zircon bricks in the zircon mud powder. The two kinds of zirconium ramming materials only need to be mixed with an appropriate amount of water in proportion, and the ramming materials will be made after mixing evenly. It is in a wet and loose state, then rammed, and sintered at high temperature to form a consolidated whole. The construction has abandoned the previous use of phosphoric acid as a binder, which is safer and more convenient.
2. Selection of 2 kinds of zirconium ramming materials
Although the two kinds of zirconium ramming materials have good corrosion resistance to glass liquid and only need extremely low pollution to glass liquid, they still need to be reasonably selected according to the properties of the produced glass.
Ramming material is composed of gas phase, crystal phase and glass phase. Although the existence of glass phase is beneficial to sintering, it has poor corrosion resistance to glass liquid compared with crystalline phase, which is the weak link of corrosion resistance of ramming material and other refractory materials. And the content has an important influence on the application function of the ramming material.
The pores are the passages through which the glass liquid penetrates into the ramming material. The porosity is high and the chemical corrosion resistance of the ramming material is poor. This is because most of the pores are concentrated in the combined phase. Once the glass liquid penetrates into the ramming material, the gas phase and the glass phase are The multiphase intersection with the corrosive agent constitutes the thinnest defect of corrosion resistance. Therefore, if the chemical composition is constant, the lower the total porosity, the stronger the corrosion resistance.
The type and composition of the corrosive agent also play a great role in the corrosion resistance of the ramming material. In the glass furnace, the corrosive agent mainly refers to the high-temperature glass liquid and the dense metal or metal oxide deposited at the bottom of the tank. The influence of molten glass on the ramming mass is different, and the characteristic rate and corrosion form of corrosion are very different between soda lime silica glass, borosilicate glass, lead glass and other types of glass.
The main difference between the fused zirconium corundum ramming material and the zircon ramming material lies in the content of Al2O3 and porosity, because the pavement located on the upper layer of the zirconium ramming material has a masonry gap, and the glass liquid will penetrate through the brick gap. Entering the ramming layer, the anti-corrosion function of the ramming material will vary due to the chemical composition of the glass liquid, the moving speed and the temperature. The soda-lime-silica glass melt is highly corrosive. When they are in contact with the ramming material, the ionized alkali is the driving force of the corrosion mechanism. The same viscosity of the melt has a great influence on the corrosion rate, no matter which glass system is in the range. The corrosion effect decreases with the viscosity and increased sharply.
The following is a further description of the effects of zircon-based ramming materials and fused AZS-based ramming materials when they are in contact with alkaline glass liquid:
(1) The fused AZS ramming material is in contact with the alkaline glass liquid, and the touch interface constitutes an aluminum-containing (Al2O3) layer. The ZrO2 in the ramming material is dissolved in the glass liquid to a very low degree, the viscosity is added, and the interface layer is dull. The chemical properties of the ramming material are resistant to mechanical wear, and the resistance to chemical corrosion is enhanced.
(2) The zircon ramming material is in contact with the alkaline glass liquid, because there is no aluminum in the zircon ramming material, the zircon is easily differentiated, and the differentiated 2 silica will reduce the viscosity and then accelerate the corrosion , resulting in damage to the ramming layer.
Therefore, the fused AZS ramming material is more suitable for the bottom ramming layer of soda lime silica glass, electric vacuum glass and other alkali glass furnaces, while the zircon material is more suitable for weak alkalis such as borosilicate. The ramming layer of the bottom of the glass furnace.
Related Industry Knowledge
- Features and Benefits of Coil Clay
- What are the advantages of a good furnace lining
- Misunderstandings in the use of ramming materials in intermediate frequency furnaces
- Phenomenon analysis of failure of argon blowing of ladle permeable bricks and how to improve the rate of argon blowing
- Where is the consumption reduction and energy saving of breathable bricks reflected?
- How to improve the service life of intermediate frequency furnace lining
- Reasons for damage to intermediate frequency furnace lining and how to solve them
- The performance and advantages of breathable brick
- Analysis of Structural Characteristics of Dispersive Breathable Bricks
- The intermediate frequency furnace charge knotting process needs to pay attention to details sharing
- Matters needing attention in the knotting process of wear-resistant ramming material
- How to use electric furnace lining to repair electric furnace
- Ramming material manufacturers tell you the influence of sliding nozzle refractories on breakout
- What should be paid attention to in material selection of intermediate frequency furnace charge
- Introduction to the construction of furnace lining ramming material
- What material is used for the lining of the intermediate frequency furnace?
- What reasons will affect the service life of the intermediate frequency furnace lining?
- What should be paid attention to in material selection of intermediate frequency furnace charge
- Ramming material manufacturers tell you how to improve the crack resistance of explosion-proof refractory castables
- Importance and characteristics of raw material structure of intermediate frequency furnace charge