Luoyang Quantong Kiln Industry Co., Ltd. has summed up the refining technology of intermediate frequency induction furnace through the use of gas diffuser, so that ordinary intermediate frequency induction furnace can be converted from chemical steel to steelmaking. In many cases, the quality of molten steel (alloy) has reached the AOD furnace. , LF refining furnace, VD vacuum degassing furnace refining quality level.

Advantages of using a gas diffuser:
1. Promote inclusions in molten steel to float, reduce inclusions, and improve the quality of molten metal;
2. Improve the use effect of additives;
3. Reduce scrap rate;
4. Extend the life of the furnace lining;
5. Low investment;
6. Endow the induction furnace with refining function to provide strong technical support for improving the quality of molten metal and developing new products.
First, the installation method of the gas diffuser

1.1 Preparation before installation
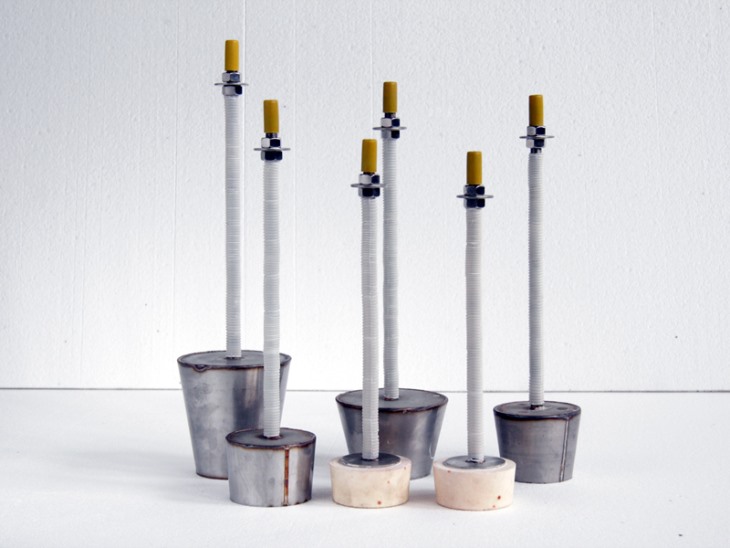
1) Process a round hole of about ¢18mm in the center of the bottom of the induction furnace shell (part of the furnace shape has been reserved) for the installation of the gas diffuser pipe.
2) Brush the H-class insulating paint on the induction coil and applyCoil Clay, Some furnaces are still laying mica board, asbestos cloth, etc. on the inner wall of the coil cement.
3) Prepare a metal tube with a wall thickness of 1-2mm and a diameter according to the size of the furnace, generally 200-350mm, height 250-300mm, and the outer surface is flat and clean. To facilitate extraction, 2 handles can be welded.
4) Prepare the gas source, such as bottled argon, nitrogen, etc., the gas purity is required to be 99.99%. When the gas consumption is large, several gas cylinders can be combined to form a manifold; a pressure gauge (range 0- 2Mpa), flow meter (range 0-250L\/min), needle valve (control airflow); in industrial mass production, the "gas intelligent control system" (available from our company) can be installed to make the gas efficient, intelligent, and Reliable control (see the company's product catalog or website for details).
1.2 Install the gas diffuser
After the above preparations are completed, pass the rear pipe of the gas diffuser (the rear pipe of the diffuser is an external thread, M162mm) through the bottom round hole, fix it on the bottom of the furnace with a nut and a gasket, and make the upper surface of the gas diffuser at the height It is about 100mm lower than the upper surface of the bottom material of the induction furnace (as shown in the figure), and the height of the upper surface of the gas diffuser is lower than or equal to the height of the bottom circle of the induction coil. After the diffuser, the pipe is connected to the adapter (pagoda head) , and then connect with the gas cylinder hose; you can also directly connect the metal hose to the rear pipe of the gas diffuser to ensure that each gas pipeline interface does not leak (as shown in the figure). Special attention: there must be no debris, dust, etc. during the connection process. into the pipeline.
Then, cover the gas diffuser with a pre-prepared iron cylinder, calibrate the position of the iron cylinder, let the diffuser be located in the center of the iron cylinder, pour the dry vibrating material into the outside of the iron cylinder, and then install the dry vibrating material in the induction furnace according to the construction process of the induction furnace. The dry vibrating material on the outside of the iron tube is to be compact and conform to the elevation of the furnace bottom material. After the vibration and ramming of the dry vibrating material on the outside of the iron tube is completed, slowly pull out the iron tube and tear off the sticker on the gas diffuser. Paper, pour the "breathable material" into the circular pit in the center of the furnace bottom, each feeding does not exceed 100mm, ram the breathable material layer by layer, and make the height of the breathable material and the dry vibrating material at the bottom of the furnace consistent, pay attention to the use of furnace forks Do not damage the gas diffuser when the vibrator is used. After the inner ventilating material is laid, use the furnace fork to trace deep for 2-3 circles along the circumference, and insert the furnace fork tip into the circumference at the same time, and the outside is to make the ventilating material and the furnace bottom dry. The vibrating materials are properly mixed with each other at the circumference, and then the fork marks on the circumference and the upper part of the breathable material are repeatedly vibrated and rammed with a vibrator equipped with a flat head, and the gas diffuser is installed.
After that, complete the subsequent blasting process: put the steel mold core in alignment (the steel mold core should be made of steel plates with a thickness of more than 6mm, which is conducive to the sintering of the furnace lining) → hit the furnace wall according to the dry vibrating material construction process of the induction furnace. The height of the dry material reaches about 50mm from the furnace mouth → the wet material hits the upper part of the furnace wall → the wet material hits the furnace mouth and the mouth of the furnace.
2. Furnace lining sintering and test blowing

Furnace lining sintering also includes the sintering of "breathable material", which is very critical. The quality of sintering is related to the life of the furnace lining and the use of gas diffusers.
The furnace for melting steel should use dense scrap steel, such as short high-quality scrap steel as much as possible, raise the temperature to about 1100 degrees Celsius for 1 hour at a heating rate of 200-300 degrees Celsius per hour, and then heat up at a rate of 300 degrees Celsius per hour, the molten The height should rise slightly above the dry\/wet connection and hold at 1680-1700 degrees Celsius for 1-2 hours.
After the sintering and heat preservation is over, you can try blowing.
Gradually open the needle valve, manually observe and adjust the gas flow to ensure that there are bubble spots on the molten steel surface, to avoid excessive gas volume, molten steel tumbling, and exposure to the air to cause secondary oxidation and slag entrainment.