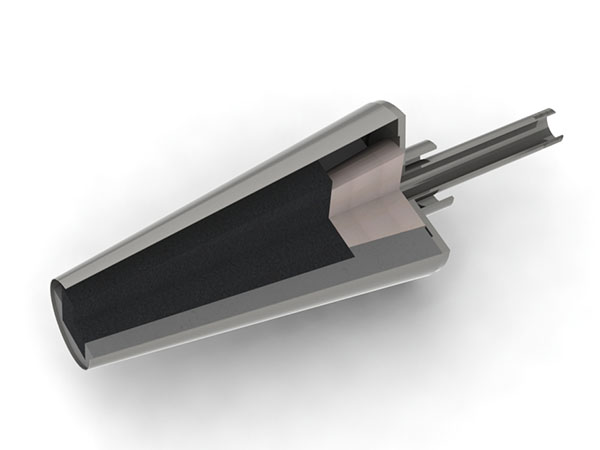
material
In order to adapt to the development of the refining process outside the furnace, the thermal shock stability of the corundum-spinel permeable brick (brick core) by the mass fraction of MgO fine powder, the change of the reburning line, the flexural and compressive strength at room temperature, the erosion index, The influence of permeability index. Through the detection and analysis of performance, it is shown that when the mass fraction of MgO increases, due to MgO and Al2O3The formation of magnesia-alumina spinel phase increases, which increases the flexural strength of the heat-treated breathable brick. And the thermal shock stability of corundum-spinel is better than the traditional chrome corundum breathable brick, but there are still some shortcomings. The volume stability is not as good as that of chrome corundum bricks.
By adding corresponding additives to the air-permeable bricks, the additives undergo a phase change during the heat treatment process to form a high-temperature solid solution phase, which has the advantages of high high-temperature strength and is difficult to be wetted by metal melt and slag. The shock resistance and slag resistance are improved.
particle size
Different particle gradations of aggregates, fine powders, binders or admixtures in the ingredients will affect the strength, flexural resistance, shock resistance and other properties of the produced breathable bricks to varying degrees.
By optimizing the particle gradation, the air-permeable brick has excellent after-fire performance and physical properties after the heat treatment process. The reasonable gradation improves the normal and high-temperature performance of the air-permeable brick, which meets the requirements of the steelmaking process.